When is GxP in the sense of GLP, GCP and GMP relevant for my company from a regulatory point of view?

Good Practices (GxP) are a set of regulations and guidelines established by regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) to ensure the quality and safety of pharmaceuticals and biotechnology products.
In the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry, GxP should be implemented throughout the entire product life cycle, from research and development to manufacturing, testing and distribution. This includes the following phases:
- Research and development: In the R&D phase, the GxP principles should be followed to ensure that the development of new medicines and biotechnology products is done in a scientifically rigorous, ethical and well-documented manner. This includes the planning of clinical trials, the selection of trial sites, the collection and processing of clinical data and the reporting of trial results. For example, clinical trials should be conducted according to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines to ensure the safety of trial participants and the validity of trial results.
- Manufacturing: In the manufacturing phase, GxP regulations should be followed to ensure the quality and consistency of medicinal products and biotech products. These include Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations, which set standards for the design, construction and operation of manufacturing facilities and for quality control procedures to ensure product quality. GMP regulations also govern the testing of raw materials, intermediate products and finished products to ensure their quality and consistency.
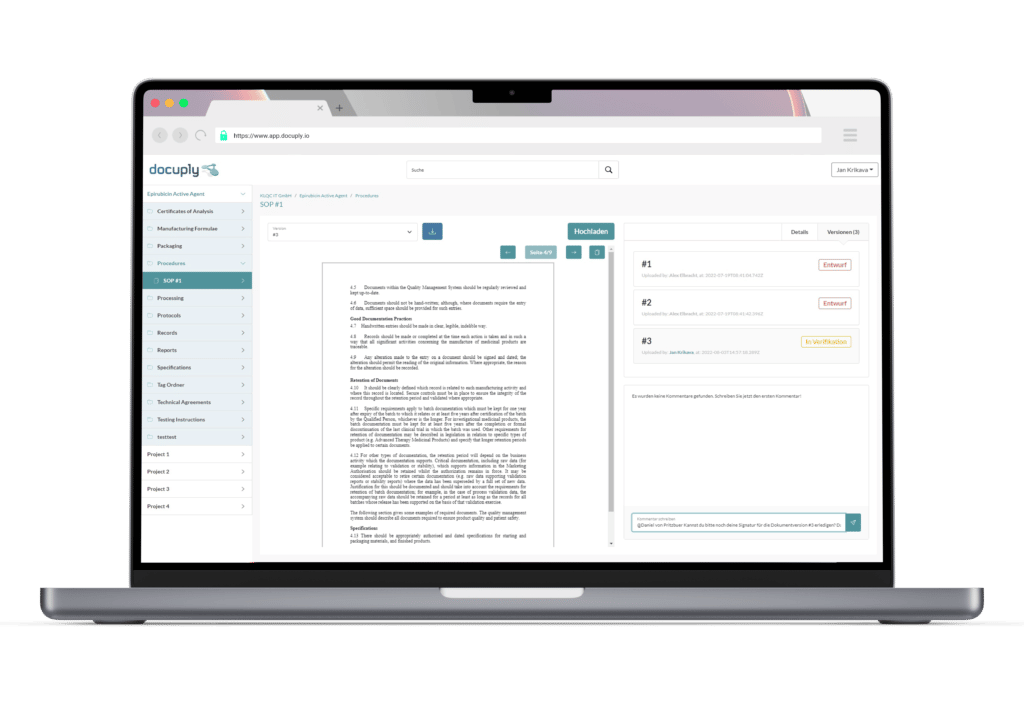
Specially developed for the pharmaceutical industry: GxP-compliant document management with Docuply, easy to use and immediately ready for use.
-
- Testing: In the testing phase, GxP principles should be applied to ensure the safety and efficacy of medicinal products and biotechnology products. These include the Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) regulations, which set standards for planning, conducting and reporting laboratory studies, and the Good Clinical Laboratory Practice (GCLP) regulations, which set standards for conducting laboratory tests in a clinical setting. The GLP and GCLP regulations ensure that laboratory studies are conducted in a scientifically rigorous, well-documented and controlled manner.
- Distribution: In the distribution phase, GxP regulations must be followed to ensure that medicines and biotech products are properly stored, transported and handled to ensure their quality and safety. This includes the Good Distribution Practice (GDP) regulations, which set standards for the storage and transport of medicinal products and biotech products, as well as for the handling of returns and recalls. The GDP regulations ensure that the conditions under which medicinal products and biotech products are stored and transported are suitable for maintaining their quality and safety, and that adequate procedures are in place for dealing with returns and recalls.
It is important to note that GxP is not a one-time implementation, but a continuous process that requires ongoing monitoring and evaluation to ensure compliance and quality throughout the product lifecycle.
Test all the advantages of a digital document management system specially developed for the pharmaceutical and biotech industry now without any obligation. You can get started in just five minutes, convince yourself.
Quality management in the pharmaceutical and biotech industry: Current challenges in the cooperation between pharmaceutical companies and CROs, CMOs and CDMOs
" The global networking and faster availability of information in large numbers are pushing our existing document management systems to their limits in terms of timely processing in compliance with GMP requirements. Therefore, we need to rethink our current way of working to enable effective and efficient document management with new IT solutions."
